Mechanical Automation
Frustrated by having to manually open/close windows and turn on/off his evaporative cooler, Adam engineered his way out of his frustration by automating it.
Proof of Concept.
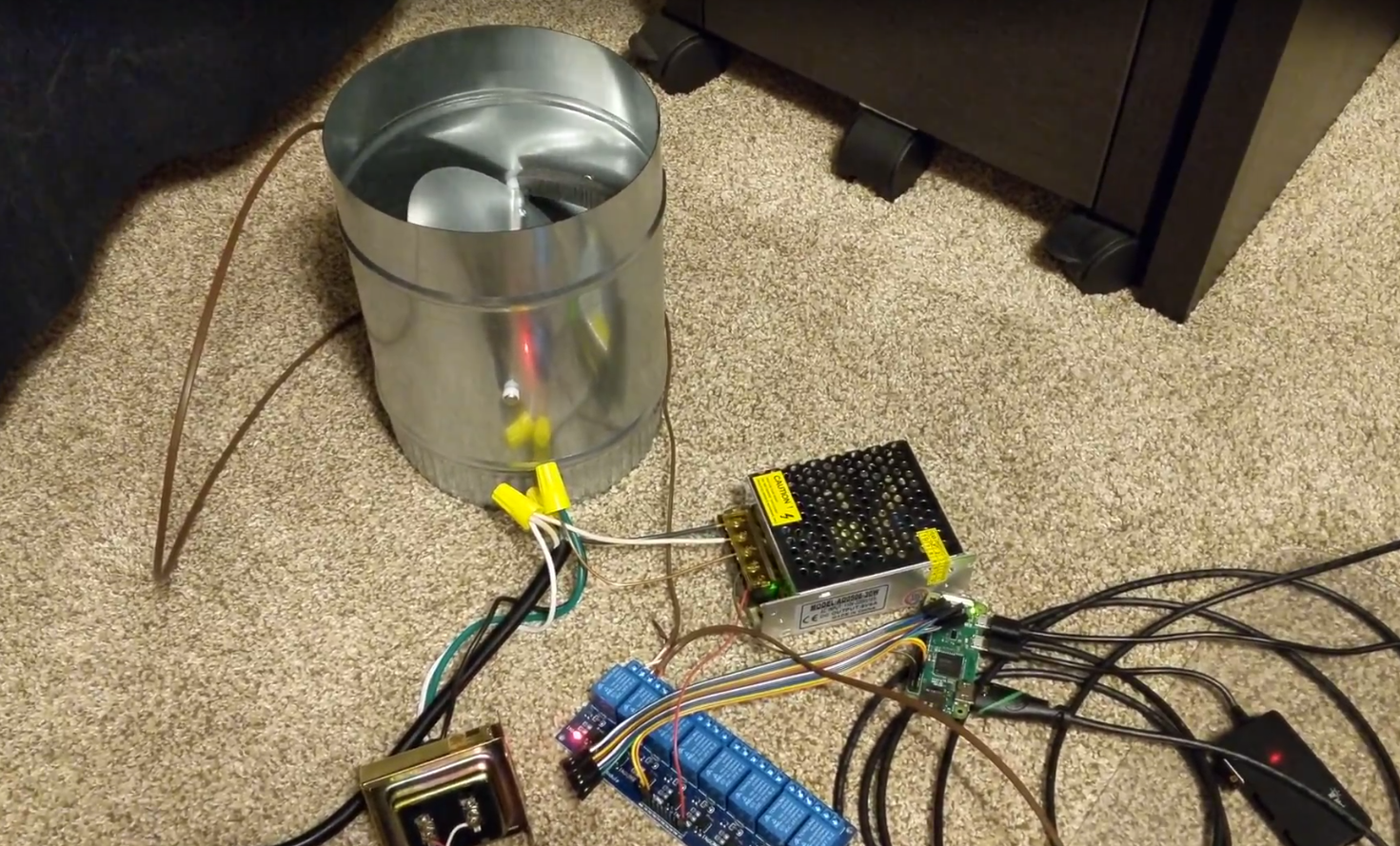
The idea was simple. Use two-position actuators to relieve air into the attic when the home was positively pressurized. A RaspberryPi Zero W would receive command messages using MQTT and energize/de-energize the appropriate relays.
Installation.
A total of five (four pictured) air relief assemblies were created and installed into the ceiling in rooms throughout the main floor of the home. Low-voltage control wires were run from the relay board to each of the two-position actuators. Additional line voltage wire was run in order to control evaporative cooler two-speed supply fan and pump.
Control Development.
The final control sequence utilized eight relays, three temperature sensors, and two humidity sensors. openHAB was used as an integration platform and provided the necessary web server and rules engine backbone. The system was setup to operate in one of seven operating modes determined by the currently sensed conditions. All the user had to do was adjust the cooling setpoint and the control algorithm would take it from there.